Payment: Focal point for Super Apps
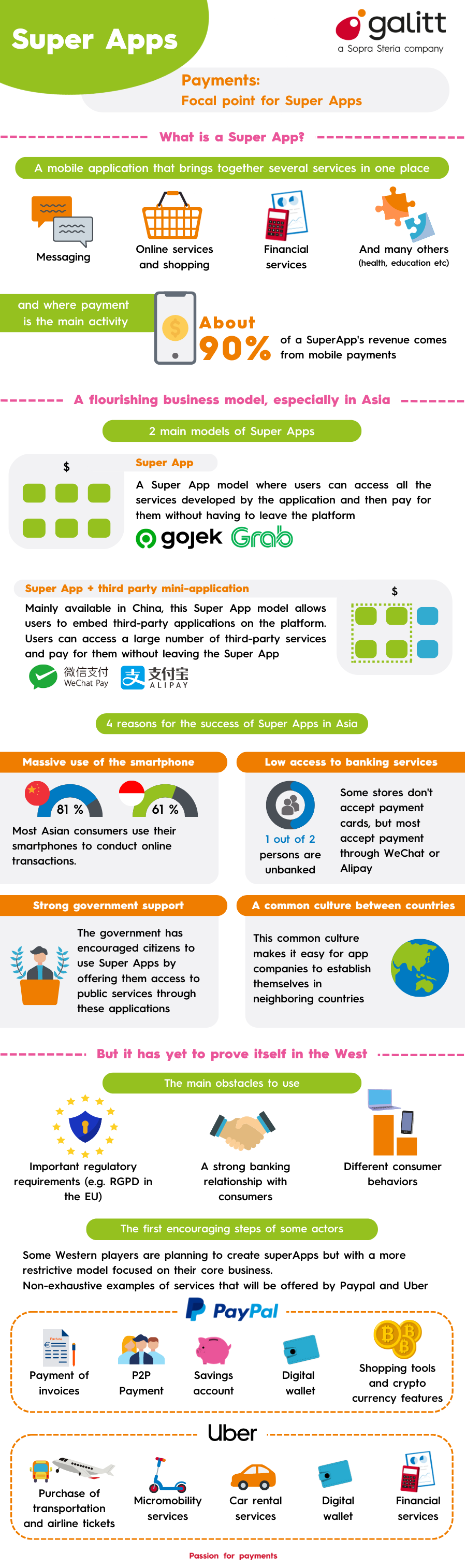
With over 3.8 trillion hours spent by consumers using mobile apps in 2021, it is not surprising that Super Apps are peaking everyone’s interest. For the consumer, the appeal comes from having an array of services (messaging, delivery, shopping, financial services, etc) easily available in one app with a seamless payment option. For a companies, a Super App touts a whole new business model allowing more revenue streams from a large diverse number of services, all centered around a native payment system.
What makes a Super App so super?
As Super Apps are widely popular in Asia, it is here that we can find the most mature and successful examples. There are essentially two main models for Super Apps. The first model is a single app with multiple features that are often made possible by a native payment system. Users can access and pay for all services without having to leave the application. An example is Gojek (Indonesian), which originally started in 2009 as a call center to connect consumers to courier delivery and ride-hailing services. Today, the Gojek app allows you to order food, buy groceries, book any kind of mobility service, buy movie tickets, pay utility bills bills and send money to friends. That is just naming some of the services available with Gojek. The user only needs to log into the Gojek, enter their payment methods, and the user can access the platform of over 20+ services instantly.
Super Apps in China take a different approach. Mobile payments and mini programs are the key features. Two popular examples are WeChat (originally a messaging service) and Alipay (originally launched as a digital wallet). These Super Apps are single applications with several functionalities, which allows third party applications to be nested on the platform thanks to a “light” and streamlined version of the application. These means the mini programs are loaded when the end user requires it, which is authorized by the Super App. These “Apps within Apps” allow users to access third-party services without leaving WeChat or Alipay and downloading a separate app. This gives the users all the convenience of accessing a diverse number of services (paying utility bills, nanny hire, food order delivery, pay hospital bill, etc) without leaving the SuperApp and most importantly, the user only needs one payment platform to pay for these services.
Payments at the front stage for Super Apps
Alipay originated in in the payment ecosystem, mainly developing its consumer-to-merchant payments ecosystem with major e-commerce and retailers in China. Tencent owned WeChat, on the other hand first started off as a messaging system and its payment inroads started with peer-2-peer payments, but has now grown to integrate a wide variety of payment services online and offline. Some examples include generating a QR code for in-store purchases for the merchant to scan, make a transfer, split a bill, do a mobile top off, or pay utilities. As diverse as the services are, payments play the central role by facilitating the entry point to these various services while ensuring engagement so users never have to leave the Super App. In fact, mobile payments are the top activity for Super Apps at nearly 90%.
Beyond payments are any services that a third party wishes to develop to run on WeChat’s platforms, essentially adding WeChat any industry’s ecosystem with their payment platform. Some western companies, such as Starbucks, has integrated into the WeChat Wallet.
The future of Super apps in the West
As popular as SuperApps are in Asia, they have not taken as strong as a hold in U.S. or Europe, despite some western companies, such as Starbucks, which has recently integrated into the WeChat Wallet.
There are several reasons behind this. First is that Asians are far more heavy users of their smartphone, as they essentially skipped the computer-based internet revolution and went directly to smartphones. Secondly, a lower access to banking services in Asia contributed to the adoption of mobile payments. In fact, some stores don’t accept payment cards but nearly all accept WeChat or Alipay payments. Finally, a strong government encouragement played a strong role, which allows the government to keep a digital contact with their population by offering access to public services via Super Apps.
The western model of Super Apps is quite different. It mainly consists in developing an increasing number of services/features in already existing applications, already built with all privacy regulations in place. The issue of data protection and privacy is of particular importance to customers in Europe and regulatory requirements are stricter. Higher access to banking services means that consumers have built as stronger relationship with their banks compared to emerging economies.
Nonetheless, some western big names are dabbling in the Super App arena, albeit a much more restrictive model. PayPal launched its first version of a Super app, offering bill pay, P2P payments, a digital wallet, shopping tools, and cryptocurrency capabilities. It also developing bank partnerships to offer savings accounts. Uber has announced its Super App ambitions, mainly in mobility by adding train, bus, plane and car rentals to their U.K. app via software integrations with mobility partners.
Although this is certainly a first step, it is a far cry from their Asian counterparts. When a consumer needs to book a taxi, order a meal, access a museum audio guide, pay the rent and book movie tickets, it would be a major shift in western consumer behaviour to think of one player as their only go-to app. Nonetheless, the average person has 80 apps installed on their phone but use an average of 9 on a daily basis. The western model may not be all encompassing, but they don’t necessarily need to be. One thing the Asian models mastered is the seamless payment journey, and this is a consumer expectation that is common. The western SuperApp has the opportunity to put payments in the forefront and enjoy the same consumer engagement benefits.